San Francisco, California. Boulder, Colorado. Washington, DC. Despite the diversity of these cities, they all have one thing in common – they rank highly on Bicycling Magazine’s list of the Top 50 Bike Friendly Cities in the U.S. What makes these cities bike friendly and what can we learn from them?
San Francisco, California. Boulder, Colorado. Washington, DC. Despite the diversity of these cities, they all have one thing in common – they rank highly on Bicycling Magazine’s list of the Top 50 Bike Friendly Cities in the U.S. What makes these cities bike friendly and what can we learn from them?
A bike friendly community is one where people feel welcomed and encouraged to ride bikes, whether for recreation, fitness or transportation. They are characterized by a culture that embraces bikes and recognizes the economic and social benefits that result from increased bicycle use. For this culture to thrive, there must be provisions that promote the use of bicycles by providing infrastructure that removes obstacles traditionally preventing people from doing so. Bike friendly communities value cycling not just as a hobby or novelty, but as a way of life.
A key benefit of these communities is an increase in the use of bikes for transportation and a decreased reliance on less sustainable forms of transport. The rising popularity of bike lanes has made it safer for riders to navigate city streets and prompted more people to bike to work. Bike lanes decrease traffic congestion and smog while providing a healthy alternative to driving. People for Bikes has done lengthy research and compiled an infographic of different types of bike lanes and the cost, benefits and effectiveness of each. There are a variety of styles to suit different urban planning designs and municipal budgets.

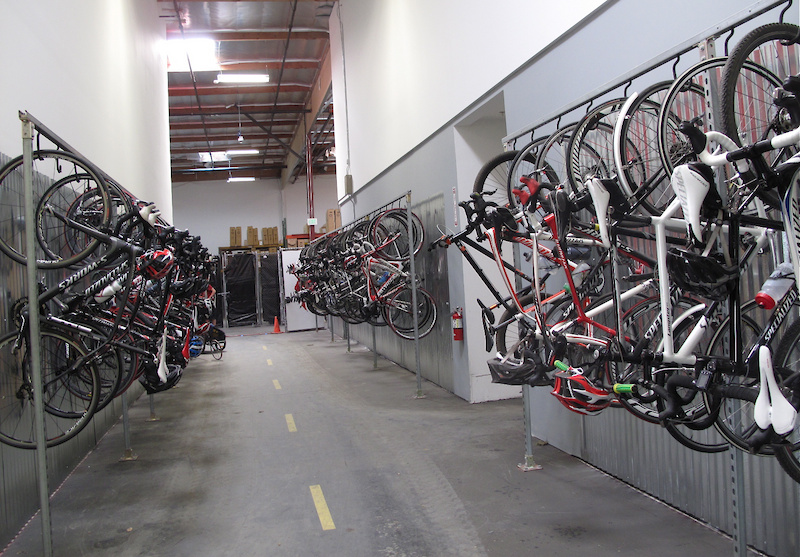
Indoor bike parking at Specialized HQ.
While providing safe routes for cyclists to take to work is necessary, it is not a standalone solution. Secure bike storage and facilities at a rider’s destination are equally important. As a leader in the industry, Specialized Bicycles’ Morgan Hill, CA headquarters offers some of the most bike-to-work friendly facilities around, including ample indoor storage and locker rooms for employees. While not every destination needs such luxurious amenities, riders expect a reasonable level of accommodation that includes secure storage and changing facilities.
The accessibility of bikes is a crucial component to the bike-friendly model; riders need somewhere to buy bikes as well as have them repaired and fit properly. The local bike shop (LBS) plays a major role by offering a variety of geographically appropriate models and offering services and accessories that enhance the riding experience. The LBS also serves as a space for bike-minded people to congregate and build social networks, strengthening the community and culture.
Most importantly, bike friendly cities rely on advocacy and cooperation between all parties. No one entity can singlehandedly create a bike friendly culture. It relies on the combined effort of all stakeholders to work towards the changes they want to see in their community.